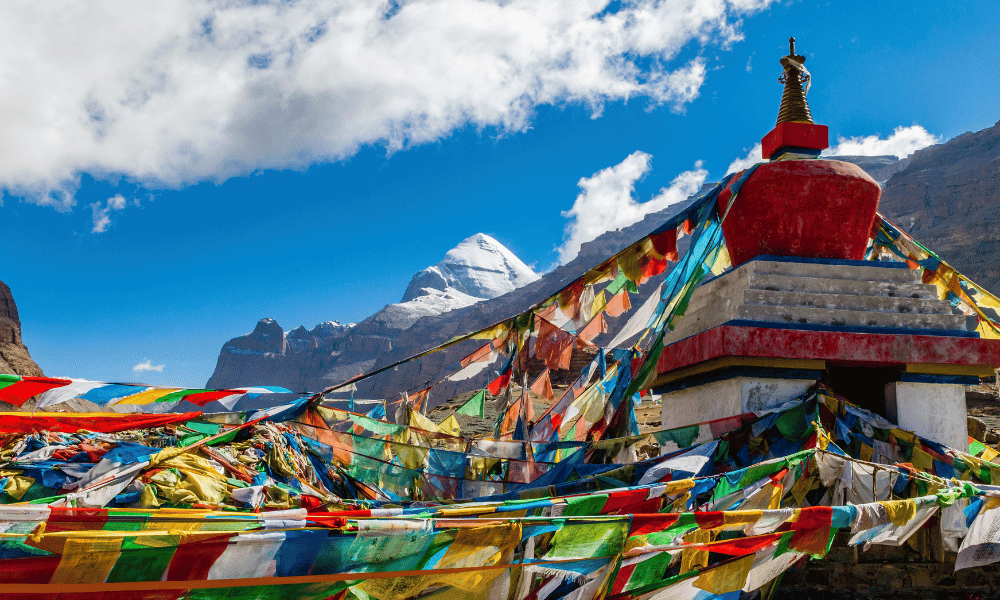
Kailash Mansarovar, a mystical destination nestled in the heart of the Himalayas, stands as a beacon for both spiritual seekers and adventure enthusiasts. Located in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, this region is renowned for its religious significance and breathtaking natural beauty. Every year, thousands of pilgrims and tourists embark on a journey to Kailash Mansarovar, drawn by the allure of its pristine lakes, towering peaks, and the promise of a life-changing experience.
Mount Kailash, often referred to as the “abode of the gods,” is considered sacred in several religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Bon. For Hindus, it is the dwelling place of Lord Shiva and his consort, Parvati. Buddhists revere it as the home of Demchok, a wrathful manifestation of Buddha. Jains believe it to be the site where their first Tirthankara, Rishabhadeva, attained nirvana. The Bon religion, indigenous to Tibet, regards it as the seat of all spiritual power.
Adjacent to Mount Kailash lies Lake Mansarovar, believed to be the highest freshwater lake in the world. According to Hindu mythology, it was created by Brahma, the creator god, and is considered a manifestation of purity. Pilgrims often take a ritual bath in its waters, believing it will cleanse them of sins and bring them closer to enlightenment.
Reaching Kailash Mansarovar is no small feat, involving a combination of air travel, road journeys, and trekking. There are multiple routes to reach the destination, with the most popular ones being via Nepal and China.
Via Nepal:
Kathmandu to Nepalgunj: The journey typically begins in Kathmandu, the capital of Nepal. From there, travelers fly to Nepalgunj, a city near the Indian border.
Nepalgunj to Simikot: A short flight takes them to Simikot, a remote town in the Humla district of northwestern Nepal.
Simikot to Hilsa: The next leg involves a helicopter ride to Hilsa, a small village on the Nepal-Tibet border.
Hilsa to Purang: After crossing the border, travelers proceed to Purang (also known as Taklakot), where they can rest and acclimatize to the high altitude.
Purang to Mansarovar: The final stretch is a road journey to Lake Mansarovar.
Via China:
Lhasa to Ali: Travelers can fly from Lhasa, the capital of Tibet, to Ali, also known as Ngari.
Ali to Mansarovar: From Ali, a road trip takes them to Lake Mansarovar.
One of the main highlights of the pilgrimage is the Kailash Kora, a 52-kilometer circumambulation around Mount Kailash. The kora is considered one of the most challenging treks in the world due to its high altitude and rugged terrain. Pilgrims believe that completing the kora erases the sins of a lifetime, while 108 circumambulations can lead to salvation.
The journey typically begins at Darchen, a small settlement at the foot of Mount Kailash. The trek is usually completed over three days:
Day 1: Darchen to Dirapuk: This part of the trek covers approximately 20 kilometers and takes trekkers to Dirapuk, where they are greeted with a stunning view of the north face of Mount Kailash.
Day 2: Dirapuk to Zuthulpuk: The second day is the most challenging, as it involves crossing the Dolma La Pass at an elevation of 5,630 meters. After the pass, the descent leads to Zuthulpuk.
Day 3: Zuthulpuk to Darchen: The final leg is a relatively easier trek back to Darchen, completing the kora.
In recent years, the Chinese government has made significant investments in improving the infrastructure and facilities for pilgrims and tourists visiting Kailash Mansarovar. This includes better roads, accommodation options, and medical facilities. In Purang and Darchen, hotels and guesthouses are offering basic amenities, including hot showers and internet access. Additionally, several travel agencies provide guided tours, ensuring that travelers have a safe and organized experience.
While the journey to Kailash Mansarovar is an awe-inspiring experience, travelers need to be mindful of the cultural and environmental sensitivities of the region. The area holds deep spiritual significance for local communities and pilgrims from around the world. Respect for local customs, traditions, and religious practices is paramount.
Moreover, the fragile ecosystem of the Himalayas requires careful stewardship. Travelers are encouraged to follow eco-friendly practices, such as minimizing waste, using biodegradable products, and respecting wildlife habitats. Sustainable tourism initiatives are increasingly being promoted to preserve the natural beauty and cultural heritage of the region for future generations.
The high altitude of Kailash Mansarovar poses significant health risks, including altitude sickness. Travelers must acclimatize properly, stay hydrated, and consult with healthcare professionals before embarking on the journey. Many travel agencies provide medical support, including oxygen cylinders and trained personnel, to ensure the safety of the pilgrims.
Kailash Mansarovar is more than just a destination; it is a transformative journey that blends spirituality, adventure, and natural beauty. Whether one is drawn by religious devotion or the allure of the Himalayas, the experience of visiting Kailash Mansarovar leaves an indelible mark on the soul. As tourism infrastructure continues to improve, it is essential to approach this sacred region with reverence and a commitment to sustainable practices, ensuring that its pristine landscapes and profound spiritual legacy endure for generations to come.