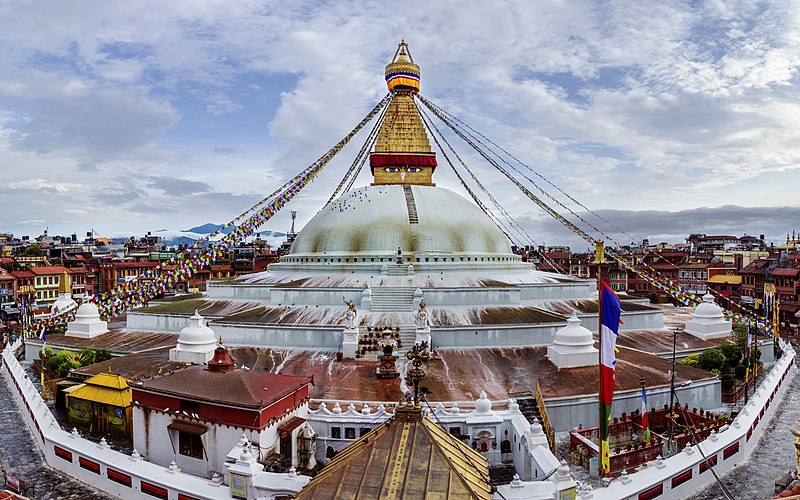
Boudhanath, one of the world’s largest stupas, is a vital symbol of Nepal’s rich cultural heritage and a major attraction for tourists globally. Situated in the heart of Kathmandu, this UNESCO World Heritage site serves both as a spiritual center for Tibetan Buddhism and a bustling hub for tourism, playing a significant role in Nepal’s economy.
Constructed in the 14th century, Boudhanath Stupa is an architectural marvel with a rich history. Its massive mandala design makes it one of Nepal’s largest spherical stupas. Surrounding the stupa is a circular market filled with shops and restaurants catering to pilgrims and tourists alike. This site is a central point for the Tibetan community in Nepal, and it is believed to house the relics of Kassapa Buddha.
Boudhanath attracts thousands of visitors each year, including pilgrims, tourists, and scholars. Its religious significance makes it a prime destination for Buddhist pilgrims from Tibet, Bhutan, India, and other countries. The influx of these visitors has fostered a vibrant economy around the stupa, supporting local businesses such as hotels, restaurants, souvenir shops, and travel agencies.
The site is particularly lively during major Buddhist festivals like Losar (Tibetan New Year) and Buddha Jayanti (Buddha’s Birthday), which draw even larger crowds and boost the local economy. These festivals showcase traditional Tibetan music, dance, and rituals, providing tourists with a unique cultural experience. Tourism centered around Boudhanath significantly contributes to the local economy. Revenue from entry fees, donations, and local businesses helps maintain the stupa and supports community projects. Additionally, the numerous monasteries and meditation centers around Boudhanath have led to a rise in spiritual tourism, attracting visitors for extended stays to participate in meditation retreats and Buddhist teachings.
Despite its popularity, Boudhanath faces challenges such as overcrowding, pollution, and the wear and tear of its ancient structures. The devastating 2015 earthquake caused significant damage to the stupa, necessitating extensive restoration efforts completed in 2016, funded largely by donations from local and international communities.
Preserving this iconic site is crucial for sustaining tourism. The Boudhanath Area Development Committee, along with various heritage conservation organizations, works tirelessly to ensure the stupa and its surroundings are preserved for future generations.
Looking ahead, there is great potential for sustainable tourism development around Boudhanath. Initiatives to improve infrastructure, promote eco-friendly practices, and enhance visitor experiences are being considered. These include better waste management systems, improved public facilities, and cultural tourism programs that educate visitors about the stupa’s history and significance.
Boudhanath stands as a testament to Nepal’s rich cultural tapestry and its pivotal role in the country’s tourism sector. By balancing preservation with tourism development, Boudhanath will continue to enchant and inspire visitors from around the world, contributing to Nepal’s cultural and economic vitality.